팩토리얼(Factorial)
- 1에서 n까지 모든 자연수의 곱(n!)
1! = 1
2! = 1x2
3! = 1x2x3

순열(Permutation)
- 순서를 정해서 나열
- 서로 다른 n개 중에 r개를 선택하는 경우의 수(순서 O, 중복 X)
ex) 5명을 3줄로 세우는 방법
ex) 서로 다른 4명 중 반장, 부반장 뽑는 방법
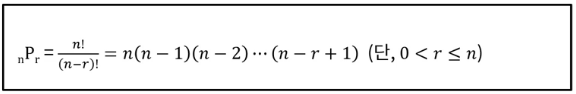
중복 순열
- 서로 다른 n개 중에 r개를 선택하는 경우의 수(순서 O, 중복 O)
ex) 서로 다른 4개의 수 중 2개를 뽑는 방법(중복 허용)
ex) 후보 2명, 유권자 3명일 때 기명 투표 방법

원 순열
- 원 모양의 테이블에 n개의 원소를 나열하는 경우의 수
ex) 원 모양의 테이블에 3명을 앉히는 경우

실습 코드
// 기초 수학 - 순열
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 팩토리얼
System.out.println("== 팩토리얼 ==");
// 5!
int n = 5;
int result = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
result *= i;
}
System.out.println("result = " + result);
// Strem구현(복습)
// range(2, 6) -> 2, 3, 4, 5 (두 번째 파라미터에 범위는 포함하지 않음)
// reduce(1 -> 초기값 1, 연산은 두 수를 곱해나가기
System.out.println(IntStream.range(2, 6).reduce(1, (x, y) -> (x * y)));// 2. 순열
System.out.println("== 순열 ==");
// 5명을 3줄로 세우는 경우의 수
n = 5;
int r = 3;
result = 1;
// 5P3
for (int i = n; i < n - r +1; i--) {
result *= i;
}
System.out.println("result = " + result);// 3. 중복 순열
System.out.println("== 중복 순열 ==");
// 서로 다른 4개의 수 중 2개를 뽑는 경우의 수 (중복 허용)
n = 4;
r = 2;
result = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
result *= n; // n의 r승
}
System.out.println("result = " + result);
// Math 함수
System.out.println(Math.pow(n, r));// 4. 원 순열
System.out.println("== 원 순열 ==");
// 원 모양의 테이블에 3명을 앉히는 경우의 수
n = 3;
result = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
result *= i;
}
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
}순열 연습 코드1
// Practice1
// 1, 2, 3, 4 를 이용하여 세자리 자연수를 만드는 방법 (순서 O, 중복 x)의 각 결과를 출력하시오
// 4개 중 3개 뽑는 것 -> 4P3 -> 4x3x2 = 24개의 결과가 나와야 함
// 방법 1
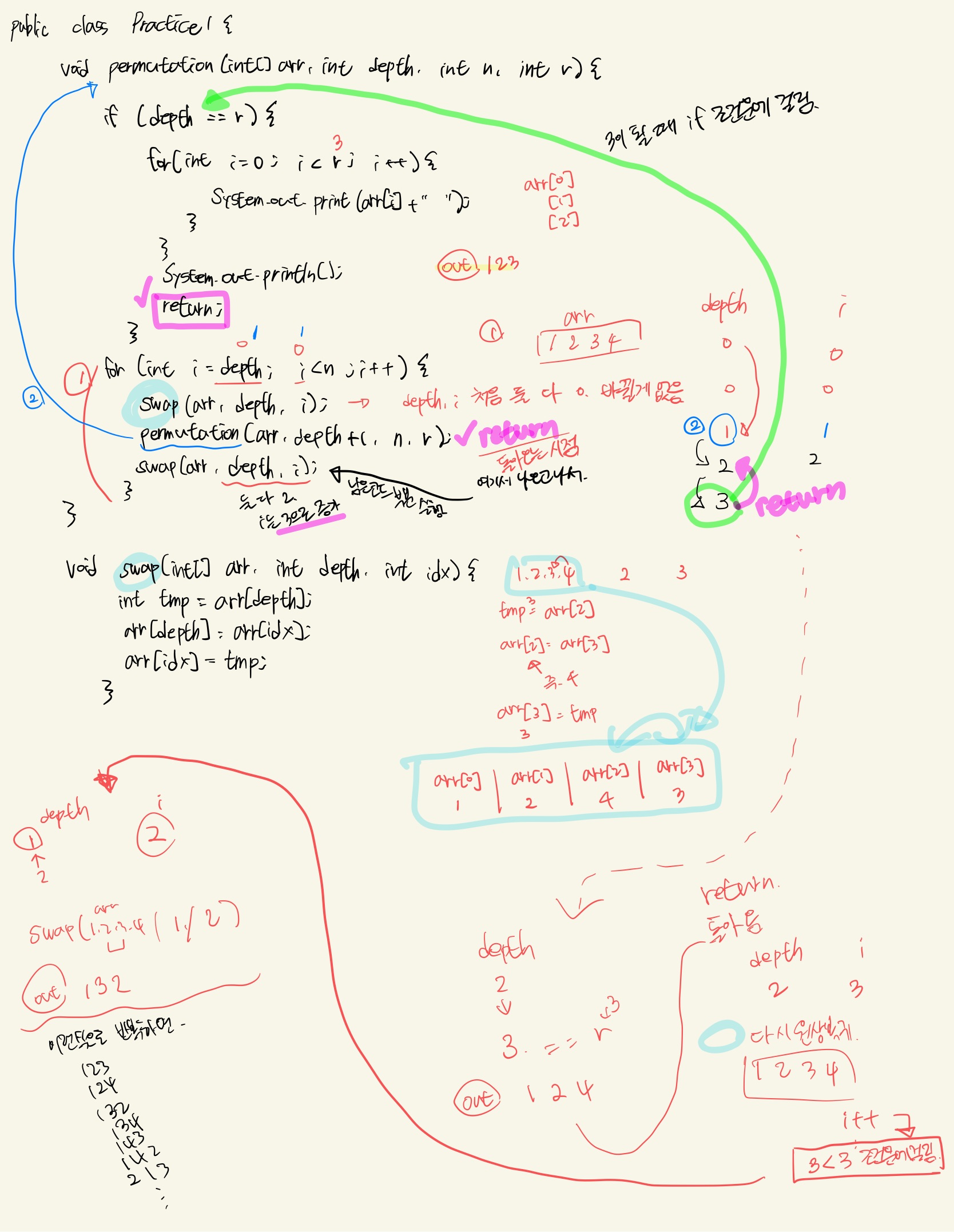
public class Practice1 {
void permutation(int[] arr, int depth, int n, int r) {
// 재귀함수 구조: 자기 자신의 함수를 계속 콜하다보니, 어느 순간은 탈출 조건이 꼭 있어야 함
// 이 자체가 반복문이 되는 것이라서 탈출 조건이 반드시 있어야 함
// 재귀함수에 대한 연습은 재귀함수 파트에서 더 자세히 배우는 것으로.
if(depth == r) {
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
for (int i = depth; i < n; i++) {
swap(arr, depth, i); // 자리를 바꾼 후
permutation(arr, depth + 1, n, r); // permutation 호출하고
swap(arr, depth, i); // 위 과정이 끝나면 다시 원래대로 자리를 바꿔주고
}
}
// 자리바꿈하기(swap)
// 배열, 몇 번째 자리수인지, 어디랑 위치를 바꿀 것인가 하는 인덱스
void swap(int[] arr, int depth, int idx) {
int tmp = arr[depth];
arr[depth] = arr[idx];
arr[idx] = tmp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4};
Practice1 p = new Practice1();
// depth: 각 자리수(0번쨰, 1번째, 2번째, 3번째 ... -> 3자리가 만들어지는 것), n: 개수(4개), r: 몇 자리(3자리)
p.permutation(arr, 0, 4, 3);
}
}
순열 연습 코드2
// Practice2
// 1, 2, 3, 4 를 이용하여 세자리 자연수를 만드는 방법 (순서 O, 중복 x)의 각 결과를 출력하시오
// 방법 2
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Practice2 {
// 1에서는 하나의 배열을 가지고 그 배열에서 자리바꿈을 하면서 출력을 했다면
// 이번에는 visited 배열을 가지고 해당 자릿수를 방문했는지 안했는지 비교해가며 출력해봄
void permutation(int[] arr, int depth, int n, int r, boolean[] visited, int[] out) {
if(depth == r) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(out));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(visited[i] != true) {
visited[i] = true;
out[depth] = arr[i];
permutation(arr, depth + 1, n, r, visited, out);
visited[i] = false;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int n = 4;
int r = 3;
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4};
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
int[] out = new int[r];
Practice2 p = new Practice2();
p.permutation(arr, 0, n, r, visited, out);
}
}'자료구조 l 알고리즘 > Ch. 01. 기초 수학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 지수와 로그 (0) | 2023.03.16 |
|---|---|
| 점화식과 재귀함수 (0) | 2023.03.16 |
| 조합 (0) | 2023.03.15 |
| 경우의 수 (0) | 2023.03.14 |
| 집합 (0) | 2023.03.13 |
