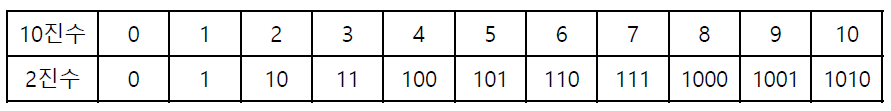
2진법
- 컴퓨터에서 데이터 표현에 사용
- 2를 기반으로 하는 숫자체계
2의 보수
- 2의 제곱수에서 빼서 얻은 이진수
ex) 2진수 3의 2의 보수 : 11 → 01
비트 연산자
- 비트 단위로 연산
- 기본 연산자와 비트 연산자 비교

비트 논리 연산자 (&, |, ^, ~)
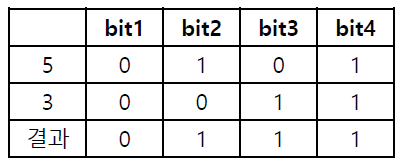
AND 연산자 (&)
- 두 개의 비트 값이 모두 1인 경우에만 결과 1

ex) 5 & 3 → 1
OR 연산자 (|)
- 두 개의 비트 값 중 하나라도 1이면 결과 1
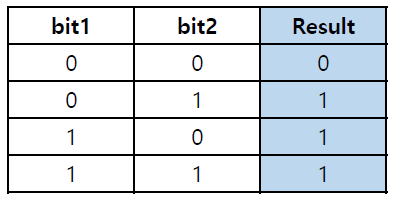
ex) 5 | 3 → 7

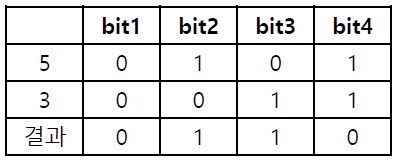
XOR 연산자 (^)
- 두 개의 비트 값이 같으면 0, 다르면 1

ex) 5 ^ 3 → 6
반전 연산자 (~)
- 비트 값이 0이면 1로, 1이면 0으로 반전
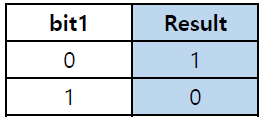
ex) ~5 → 6

비트 이동 연산자 (<<, >>, >>>)
<< 연산자
- 비트를 왼쪽으로 이동
ex) 3 << 1

>> 연산자
- 비트를 오른쪽으로 이동
ex) 3 >> 1

>>> 연산자
비트를 오른쪽으로 이동(부호비트 상관 없이 0 으로채움)
실습 코드
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 비트 논리 연산자
System.out.println("== 비트 논리 연산자 ==");
// 1-1. AND 연산자 (&)
System.out.println("== & ==");
int num1 = 5;
int num2 = 3;
int result = 0;
// 두 개의 비트 값 모두 1인 경우에만 결과 1
result = num1 & num2; // 1
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(num1));
// 4자리 수 출력. 4자리를 못미치는 경우 앞을 0으로 채워서 출력
// %d: 정수형 데이터를 받을 수 있는 서식 문자
System.out.printf("%04d\n", Integer.parseInt(Integer.toBinaryString(num1))); // 0101
System.out.printf("%04d\n", Integer.parseInt(Integer.toBinaryString(num2))); // 0011
System.out.printf("%04d\n", Integer.parseInt(Integer.toBinaryString(result))); // 0001
// 1-2. OR 연산자 (|)
System.out.println("== | ==");
result = num1 | num2;
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.printf("%04d\n", Integer.parseInt(Integer.toBinaryString(num1))); // 0101
System.out.printf("%04d\n", Integer.parseInt(Integer.toBinaryString(num2))); // 0011
System.out.printf("%04d\n", Integer.parseInt(Integer.toBinaryString(result))); // 0111
// 1-3. XOR 연산자 (^)
System.out.println("== XOR ==");
result = num1 ^ num2;
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.printf("%04d\n", Integer.parseInt(Integer.toBinaryString(num1))); // 0101
System.out.printf("%04d\n", Integer.parseInt(Integer.toBinaryString(num2))); // 0011
System.out.printf("%04d\n", Integer.parseInt(Integer.toBinaryString(result))); // 0110
// 1-4. 반전 연산자 (~)
System.out.println("== ~ ==");
num1 = 5;
result = ~num1;
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.printf("%04d\n", Integer.parseInt(Integer.toBinaryString(num1))); // 0101
System.out.printf("%s\n", Integer.toBinaryString(result)); // 부호비트 1 ~ 1010
// 2. 비트 이동 연산자
System.out.println("== 비트 이동 연산자 ==");
// 2-1. << 연산자
int numA =3;
result = numA << 1;
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.printf("%04d\n", Integer.parseInt(Integer.toBinaryString(numA))); // 0011
System.out.printf("%04d\n", Integer.parseInt(Integer.toBinaryString(result))); // 0110
// 2-2. >> 연산자
result = numA >> 1;
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.printf("%04d\n", Integer.parseInt(Integer.toBinaryString(numA))); // 0011
System.out.printf("%04d\n", Integer.parseInt(Integer.toBinaryString(result))); // 0001
// 2-3. >>> 연산자
numA = -5;
result = numA >> 1;
System.out.printf("%s\n", Integer.toBinaryString(numA));
System.out.printf("%s\n", Integer.toBinaryString(result));
// >>>는 오른쪽으로 비트이동을 시켜주면 앞에 0이 있는데 생략된 것
// 비어있는 비트가 0인 것
result = numA >>> 1;
System.out.printf("%s\n", Integer.toBinaryString(numA));
System.out.printf("%s\n", Integer.toBinaryString(result));
}
}GoodNotes

